Introduction: From Sci-Fi Dreams to Tangible Reality
Humanoid robots have captured the public’s imagination for decades. Early depictions in movies and literature painted them as both saviors and potential threats, embodying human-like traits that could either assist or rival mankind. Today, however, we see a gradual transformation. Advancements in artificial intelligence and robot technology have propelled these machines out of the realm of fantasy into practical applications in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and even customer service.
The rapid pace of robotics evolution means that innovations once reserved for the pages of science fiction are now becoming accessible realities. Yet, the path to widespread adoption is not without obstacles. High initial costs, technical challenges, usability issues, and ethical dilemmas continue to shape the development and public acceptance of these human-like robots. This article provides an in-depth exploration of these factors, aiming to deliver a balanced view of both the promises and the challenges of humanoid robotics.
Demystifying Humanoid Robotics: A Historical Perspective

What is Humanoid Robotics?
Humanoid robotics involves the design and creation of robots that mimic the human form and behavior. From the early days of robots fiction to the current emergence of android robots, this field has undergone significant transformations. Early prototypes were often clunky and rudimentary, built more for experimental purposes than practical application. However, as robot automation and artificial intelligence have matured, so too have the capabilities of these machines.
Engineers design modern humanoid robots not only to resemble humans in appearance but also to perform tasks in intuitive and efficient ways. These robots often incorporate advanced sensors, actuators, and control systems that allow them to interact with their environment dynamically. As a result, the boundary between science fiction and practical robotics has become increasingly blurred.
A Journey from Science Fiction to Reality
The journey from conceptual designs in science fiction robots to operational real life humanoid robots is marked by several key milestones. Early works of fiction, such as those depicting sentient androids and intelligent machines, inspired researchers to explore the possibilities of building human-like machines. Over the decades, technological advancements in computer science, mechanical engineering, and materials science have allowed for more sophisticated designs that closely mimic human motion and decision-making.
Historically, people viewed humanoid robots as novelties—mechanical replicas meant to showcase technological prowess rather than serve functional roles.However, as research advanced, these robots began to offer practical applications. Today, industries not only use them in industrial settings but also integrate them into service roles, demonstrating the real-world impact of human-like artificial intelligence and advanced robotics.
Investing in the Future: Cost and Affordability

High Initial Investment and Ongoing Maintenance
The high cost of both initial acquisition and ongoing maintenance significantly hinders the widespread adoption of humanoid robots.Research and development in this field require substantial financial investment. State-of-the-art ai humanoid robots often incorporate cutting-edge technology that is expensive to produce and maintain. This includes high-quality sensors, advanced processors, and robust mechanical components that ensure durability and performance.
For businesses and consumers alike, the prospect of investing in such technology can be daunting. The high cost goes beyond the initial purchase, encompassing software updates, hardware maintenance, and repairs. As manufacturers continue to innovate, there is a crucial need to strike a balance between performance and affordability. Understanding these cost structures is essential for potential adopters and investors.
Commercial vs. Consumer Models
A significant factor affecting cost is the differentiation between commercial-grade and consumer-grade models. Commercial-grade humanoid robots handle heavy-duty tasks in industrial or enterprise environments. These models prioritize robustness, reliability, and scalability, making them suitable for tasks that require high performance over extended periods. On the other hand, consumer-grade robots, while more affordable, often lack the advanced functionalities and durability of their commercial counterparts.
The decision between these models depends largely on the intended application. For instance, a manufacturing plant may benefit more from a commercial-grade robot with high precision and reliability, whereas a consumer looking for a personal assistant robot might opt for a more cost-effective model that offers basic functionalities. This dichotomy is essential to consider when evaluating the overall investment in humanoid robotics.
Manufacturers are continually seeking ways to reduce costs without compromising on quality. Advances in mass production techniques, improved component sourcing, and streamlined design processes are all contributing factors that may help bring down the overall price of these machines in the future.
Engineering Marvels or Technical Hurdles? Navigating AI and Performance

Programming Challenges and AI Integration
At the heart of humanoid robotics is the integration of advanced artificial intelligence. Despite significant progress, developing robust and reliable AI for humanoid robots remains one of the most challenging aspects. Programming these machines to interpret complex data, learn from their interactions, and make decisions in real-time requires sophisticated algorithms and extensive computational power.
One of the key challenges is creating systems that can adapt to new situations as effectively as humans do. While ai humanoid robots can perform predefined tasks with high precision, their ability to handle unexpected scenarios or novel tasks often lags behind human capabilities. This limitation stems from the inherent complexity of designing algorithms that can emulate human decision-making processes.
Furthermore, the integration of AI into humanoid robots is not merely a technical exercise—it also involves overcoming barriers related to data privacy, security, and ethical considerations. Developers must ensure that these systems are not only efficient but also safe and secure, which adds an additional layer of complexity to the programming process.
Movement, Adaptability, and Real-Time Decision-Making
The physical performance of humanoid robots is another area where significant challenges persist. While researchers have made impressive strides in replicating human movement, these machines still face notable limitations in adaptability and agility. Modern humanoid robots can perform basic locomotion tasks, such as walking or picking up objects, but they often struggle with complex movements that require balance, precision, and adaptability.
The real-time decision-making capabilities of these robots are also a subject of ongoing research. For instance, navigating through dynamic and unpredictable environments remains a significant hurdle. Human beings can effortlessly adjust their movements based on sensory feedback, but replicating this level of responsiveness in robots is a formidable challenge.
Despite these technical limitations, the potential benefits of overcoming these hurdles are immense. Enhanced movement and real-time decision-making would enable humanoid robots to perform a broader range of tasks, from assisting in emergency situations to performing intricate surgical procedures. Researchers are continuously exploring new methods—ranging from machine learning enhancements to novel sensor technologies—to bridge this gap between expectation and performance.
Bridging the Gap: Intuitive Interfaces and Everyday Usability
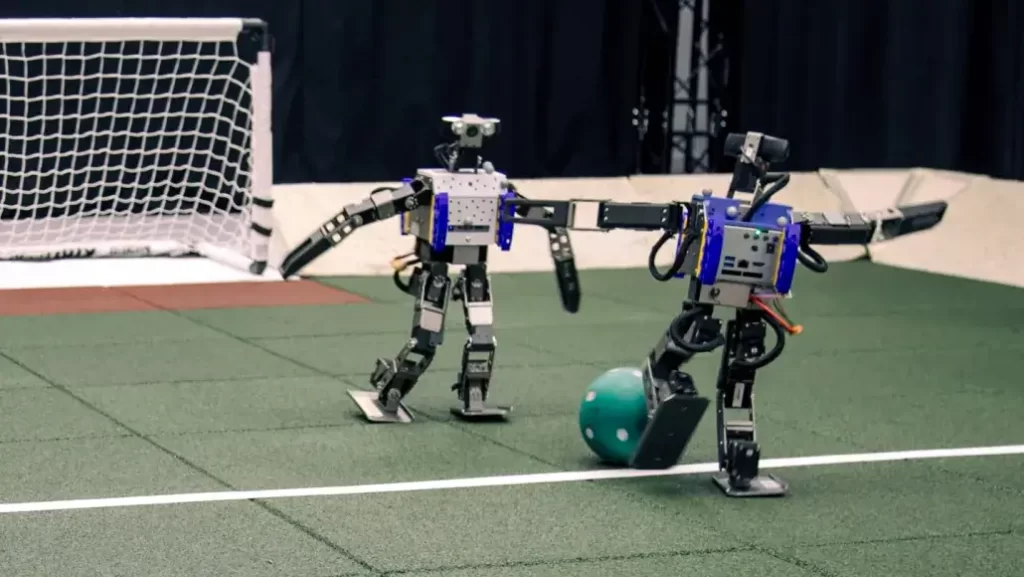
Ease of Use for Non-Experts
For humanoid robots to become a common sight in everyday life, they must be accessible to users who are not robotics experts. The complexity of operating these machines has historically been a significant barrier to broader adoption. Early models required specialized knowledge to operate and maintain, limiting their usability in non-industrial settings.
Recent developments, however, have focused on creating more intuitive interfaces and interaction models that cater to the average user. These advancements include voice-activated commands, touch-screen controls, and even gesture-based interfaces that simplify user interaction. The goal is to make human-like robots as user-friendly as possible, ensuring that individuals without a technical background can easily benefit from their capabilities.
Enhancing User Experience in the Workplace
The workplace is one of the most promising arenas for the integration of humanoid robots. In many industries, these robots handle repetitive tasks, provide customer service, and assist with complex processes. Their ability to work alongside humans—rather than replace them—has been a key selling point.
Manufacturers are incorporating intuitive controls and streamlined user interfaces to help employees work effectively with these machines. This not only improves operational efficiency but also helps to mitigate fears regarding job displacement. The narrative is shifting from robots as threats to robots as valuable partners in the workplace, highlighting the benefits of robots in the workplace and the potential for a collaborative future.
Moreover, the integration of humanoid robots into daily business operations is paving the way for more innovative applications. For example, in customer service settings, robots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up human staff to manage more complex issues. In industrial environments, they can perform hazardous tasks, thereby improving workplace safety. As these applications expand, the overall user experience is expected to improve significantly.
Keeping Up with Robots: Reliability and Maintenance

Long-Term Durability and Support
Reliability is a critical factor in the acceptance of humanoid robots. For these machines to be viable in everyday scenarios, they must demonstrate long-term durability and consistent performance. This means that, beyond initial functionality, ongoing support and maintenance are crucial to keep these systems operational over time.
Manufacturers are focusing on developing robust hardware and software solutions that can withstand the rigors of daily use. This involves designing components that resist wear and tear and creating modular systems that can be easily repaired or upgraded. Long-term support is particularly crucial for commercial applications, where downtime can lead to significant financial losses.
The importance of maintenance extends beyond physical repairs. Regular software updates are necessary to keep the AI systems running efficiently and securely. These updates often include new features and performance enhancements that help bridge the gap between the current state of technology and the high expectations set by early science fiction robots depictions.
Troubleshooting and Repair Challenges
Even with advancements in durability and design, troubleshooting remains an inevitable part of the humanoid robotics lifecycle. Common issues such as sensor malfunctions, software bugs, and mechanical wear can affect performance. For both consumers and industrial users, having a reliable system for diagnosing and resolving these issues is vital.
Many companies are now offering comprehensive support packages that include remote diagnostics, on-site repairs, and easy-to-access service networks. Such initiatives reduce downtime from repairs and build trust among users by ensuring help is readily available when needed. By addressing these challenges, the industry aims to make human-like robots more reliable and appealing to a wider audience.
Ethics and Safety: Navigating the Risks of Human-Like Robots
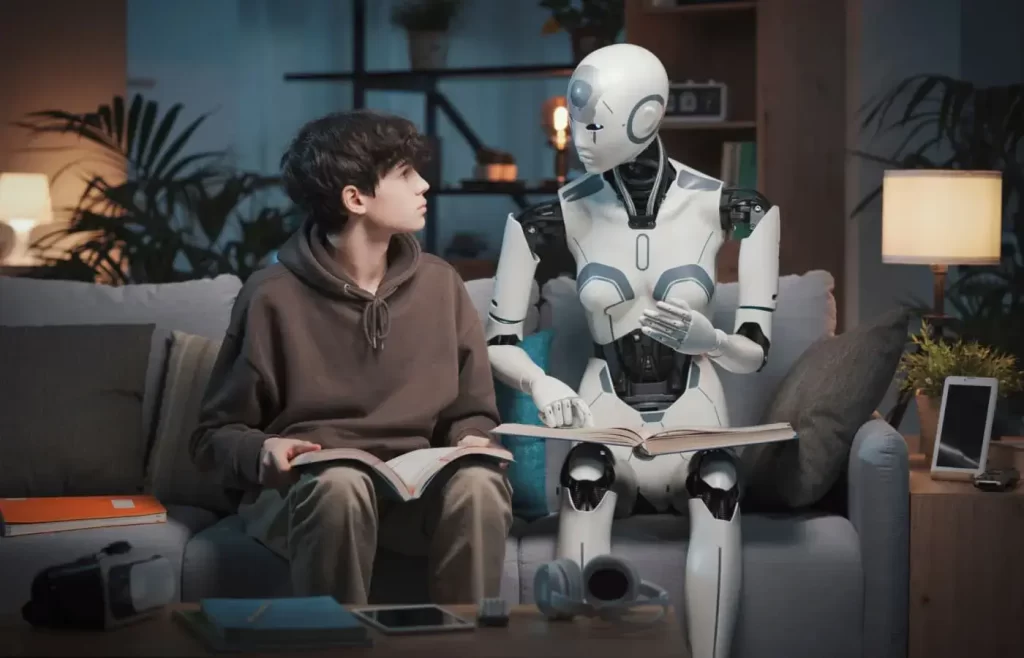
Ensuring Safe Operation in Human Environments
Safety is perhaps the most critical factor when introducing humanoid robots into environments that are shared with humans. These machines must be designed to operate safely in various settings, ranging from crowded public spaces to busy industrial floors. This involves rigorous testing, adherence to strict regulatory standards, and the implementation of advanced safety protocols.
Modern humanoid robots come with sensors that detect obstacles, monitor human presence, and adjust their operations as needed. Despite these measures, the possibility of malfunction or unpredictable behavior remains a concern. Manufacturers must continuously update safety features and emergency response systems to prevent accidents and maintain a secure operational environment.
Regulatory bodies around the world are also playing a significant role in setting standards for robotic safety. These guidelines help ensure that as anthropomorphic robots become more prevalent, they do so in a manner that minimizes risk to human life and property. Ensuring compliance with these standards is not only a legal necessity but also a crucial factor in gaining public trust.
Privacy, Security, and Ethical Implications
Beyond physical safety, the ethical implications of humanoid robotics are significant. The integration of advanced AI systems into machines that closely mimic human behavior raises important questions about privacy, data security, and the ethical treatment of intelligent systems. With human-like artificial intelligence comes the responsibility to ensure that these systems are not misused or exploited.
Privacy concerns are paramount, especially as these robots are equipped with cameras, microphones, and other sensors that continuously collect data from their surroundings. Ensuring that this data is securely stored and ethically managed is critical. Moreover, as these robots become more integrated into our daily lives, discussions around their role in society—and the potential for them to replace human interaction—must be addressed transparently.
Ethically, the design of android robots and ai humanoid robots also touches on issues of autonomy and control. Who is responsible when a robot makes a decision that results in harm? How should intellectual property and machine learning data be managed? These questions are at the forefront of debates among engineers, ethicists, and policymakers. The answers will shape the future of humanoid robotics and influence public acceptance on a global scale.
Embracing the Future: Integration and Social Acceptance

Daily Life and Workplace Integration
The integration of humanoid robots into daily life is a gradual yet transformative process. Today, we see examples of human-like robots being used in retail, healthcare, and education—fields that were once considered exclusively human domains. In the workplace, robots are becoming collaborators rather than competitors, handling tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or require precision beyond human capabilities.
As these machines become more commonplace, their presence is reshaping the way we think about labor and productivity. For instance, in manufacturing, humanoid robots are increasingly being deployed to work alongside human operators, enhancing overall efficiency and safety. Similarly, in customer-facing roles, these robots can offer consistent service, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction. The narrative is shifting to view robots in the workplace as vital partners who bring significant benefits without replacing human ingenuity.
Impact on Employment and Social Dynamics
Despite the clear advantages, the integration of humanoid robots also raises concerns about job displacement and shifts in social dynamics. While automation has the potential to eliminate certain repetitive tasks, it also creates opportunities for new types of employment. The challenge lies in managing this transition effectively. Governments, educational institutions, and industries must collaborate to retrain workers and prepare them for a future where robotics evolution plays a central role.
Social acceptance of humanoid robots depends largely on how well these concerns are addressed. Public perception is influenced by how these machines are portrayed in the media and by personal experiences with technology. As anthropomorphic robots become more integrated into daily life, it will be important to foster a narrative that emphasizes collaboration and mutual benefit rather than fear and displacement. Ultimately, the goal is to build a future where humans and robots can coexist in a symbiotic relationship that enhances productivity, creativity, and quality of life.
From Sci-Fi Promises to Reality: Evaluating Performance
Functionality vs. Expectations
One of the most compelling aspects of humanoid robotics is the gap between the lofty promises of sci fi humanoid robot depictions and the current reality of their performance. Science fiction has long painted a picture of robots that are indistinguishable from humans—not only in appearance but also in their cognitive and physical abilities. In practice, however, most humanoid robots today still fall short of these expectations.
The reality is that while modern machines are impressive, they are limited by the current state of technology. Most humanlike robots can perform specific tasks very well, but they lack the comprehensive versatility and intuitive decision-making skills of a human being. Bridging this gap is a primary focus of ongoing research. Efforts are being made to enhance machine learning algorithms, improve sensor integration, and develop more advanced control systems that can better mimic human cognition and movement.
Future Trends and Developments
Looking forward, the evolution of humanoid robotics promises exciting developments. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate more advanced forms of human-like artificial intelligence into these systems, making them more adaptable and capable of handling a wider range of tasks. Innovations in materials science and mechanical engineering are expected to lead to robots that are not only more durable but also more agile and responsive.
The next generation of humanoid robots will likely see significant improvements in their ability to interact with humans. As interfaces become more intuitive and AI algorithms more sophisticated, these robots will be better equipped to understand and respond to human emotions and commands. This progress will further blur the lines between science fiction and reality, gradually fulfilling the promise of truly human-like machines.
Moreover, the ongoing collaboration between technology developers and regulatory bodies will help establish standards that ensure safety and ethical use. As these frameworks mature, public confidence in humanoid robotics is expected to grow, paving the way for broader social acceptance and integration into everyday life.
Conclusion
In summary, the future of humanoid robotics is poised on the brink of significant breakthroughs. The path from science fiction to everyday reality is complex, characterized by challenges that require innovative solutions and collaborative efforts across multiple disciplines. As researchers, engineers, and policymakers work together to address these hurdles, the potential for humanoid robots to transform industries, enhance human productivity, and improve quality of life becomes increasingly tangible.
The evolution of human-like robots is not merely a technological trend—it is a reflection of our aspirations to merge the best of human ingenuity with the precision and efficiency of machine intelligence. As we stand at this intersection of science and fiction, the ongoing advancements in humanoid robotics promise to reshape our world in profound ways, bringing us ever closer to a future where these intelligent machines are not just a vision in a story, but an integral part of our daily existence.